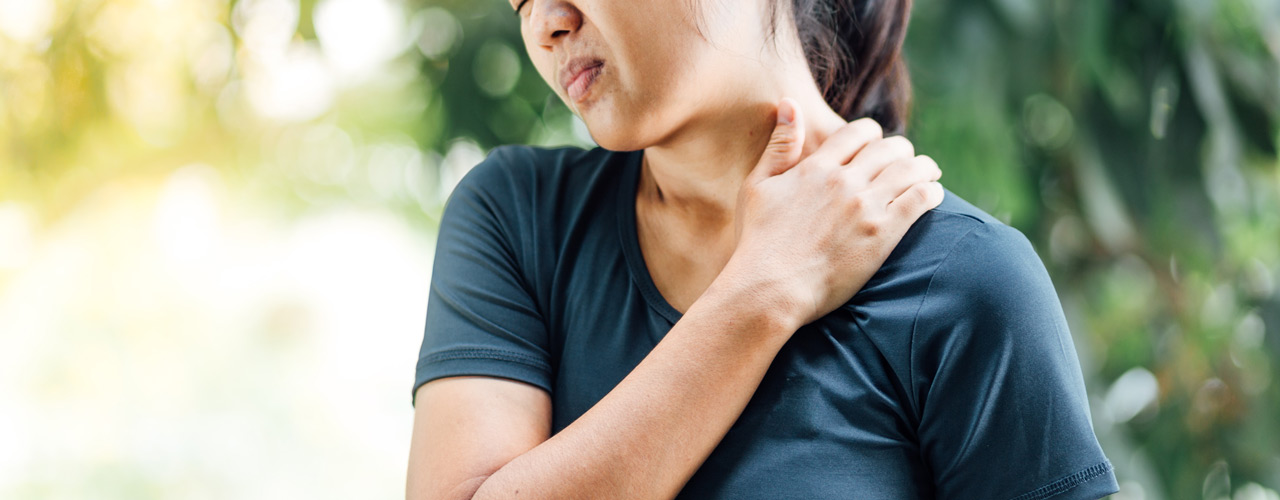
Understanding shoulder pain is crucial for effectively managing and preventing it. The shoulder is a complex and highly mobile joint, making it susceptible to various injuries and conditions. Addressing shoulder pain promptly is essential for maintaining mobility and overall quality of life. This comprehensive guide will delve into the causes of shoulder pain, symptoms, diagnostic methods, quick fixes, long-term treatments, and preventive measures to help you navigate and alleviate this common issue.
Table Of Content
Anatomy of the Shoulder
The shoulder is a ball-and-socket joint comprising three bones: the humerus (upper arm bone), scapula (shoulder blade), and clavicle (collarbone). This joint’s intricate structure includes muscles, tendons, and ligaments that provide stability and a wide range of motion. Understanding the basic anatomy of the shoulder helps in identifying the common points of injury, which often involve the rotator cuff, the group of muscles and tendons that stabilize the shoulder.
Common Causes of Shoulder Pain
Causes of shoulder pain can be varied and complex. Some of the most frequent include:
Injuries and Trauma
-
Dislocation: The humerus slips out of the socket, causing intense pain and limited mobility.
-
Rotator Cuff Tear: Can be partial or full-thickness, often from acute trauma or repetitive strain. Common in sports and manual jobs.
Overuse and Repetitive Motion
-
Tendonitis / Tendinopathy: Inflammation or degeneration of the shoulder tendons from repetitive motions (e.g., lifting, typing, sports).
-
Bursitis: Inflammation of the bursa sac, leading to pain, tenderness, and swelling.
Degenerative Conditions
- Shoulder Osteoarthritis: Age-related cartilage wear causes joint pain, stiffness, and grinding sensations.
- Calcific Tendonitis: Calcium deposits form in tendons, leading to intense pain.
Referred Pain
- Heart-related pain: Left shoulder pain may be a sign of cardiac issues like angina or heart attack.
- Gallbladder issues: Right shoulder pain can be referred from gallstones or inflammation.
- Cervicogenic pain: Neck problems (e.g., disc herniation) can refer pain to the shoulder.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Typical Symptoms
- Localized or radiating shoulder pain
- Pain when lifting the arm overhead or behind the back
- Weakness or heaviness in the affected arm
- Limited range of motion or stiffness
- Clicking, popping, or instability sensations
Diagnosis Tools
-
Physical Exam: Testing shoulder strength, movement, and tenderness points.
-
Imaging: X-rays (to rule out fractures), MRI (for soft tissue damage), and ultrasound (to visualize tendon injuries).
Quick Fixes and Immediate Relief
-
Rest: Avoid aggravating movements.
-
Ice and Heat Therapy: Apply ice to reduce inflammation, followed by heat to promote circulation.
-
Over-the-Counter Pain Medications: NSAIDs like ibuprofen help reduce swelling and discomfort.
-
Gentle Range-of-Motion Exercises: Begin with light shoulder circles or pendulum exercises under guidance.
-
Postural Adjustments: Avoid slouching and maintain ergonomic alignment during daily tasks.
Long-Term Treatment and Management
-
Physiotherapy: Tailored 1-on-1 sessions to strengthen shoulder muscles, correct posture, and promote healing.
-
Manual Therapy: Mobilization and soft tissue techniques to reduce stiffness and restore function.
-
Shockwave Therapy: Effective for chronic tendon injuries and calcific tendonitis.
-
Injections: Corticosteroid injections for bursitis, frozen shoulder, or tendonitis.
-
Surgery: For cases like full-thickness rotator cuff tears or persistent impingement syndrome.
Preventive Measures
-
Warm-up Before Exercise: Prepare the muscles to reduce strain.
-
Proper Technique: Whether lifting weights or typing, maintaining correct form is key.
-
Regular Strengthening and Stretching: Focus on rotator cuff, scapular stabilizers, and posture muscles.
-
Ergonomic Workstation: Adjust desk height, monitor position, and arm support to prevent strain.
-
Avoid Repetitive Overhead Activities: Rest between repetitive tasks to prevent overuse injuries.
When to Seek Professional Help
Seek help from a physiotherapist or medical professional if:
- Pain persists for more than 2 weeks
- You experience night pain or difficulty sleeping
- There is visible swelling or deformity
- You cannot lift your arm or perform daily tasks
Conclusion
Shoulder pain can impact every part of your life—from dressing to working. Understanding the underlying causes and acting early can prevent chronic issues. At Mobilize Physio, our physiotherapists provide evidence-based, personalized care to help you move freely and live pain-free. Book an assessment today and take the first step towards healthier shoulders.


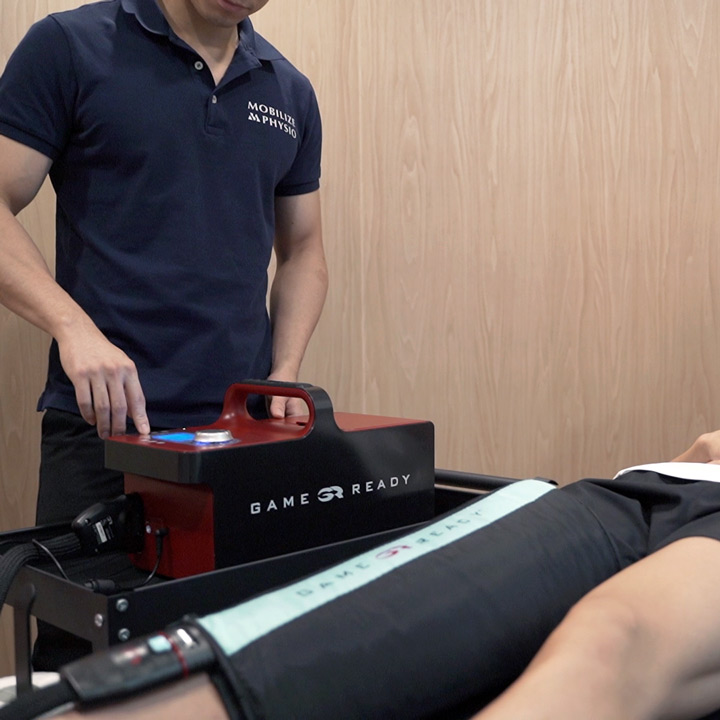

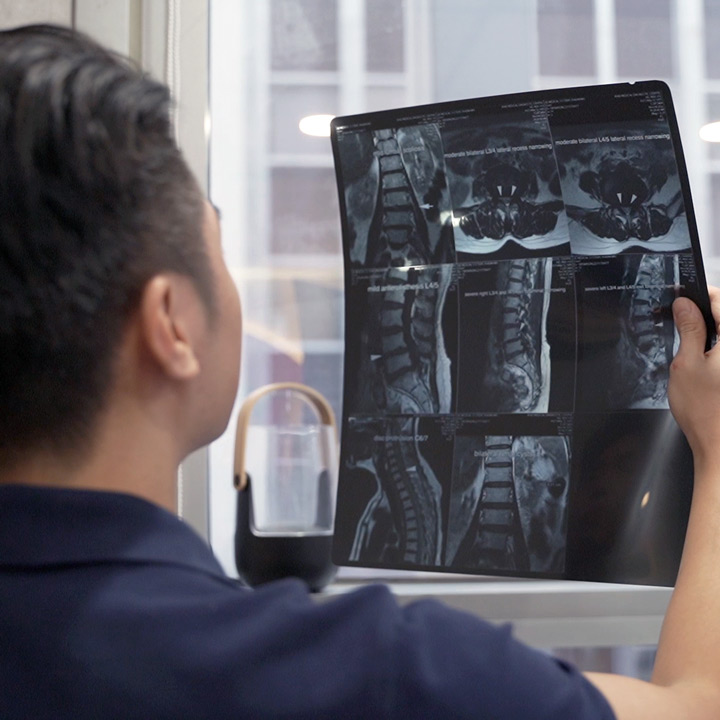
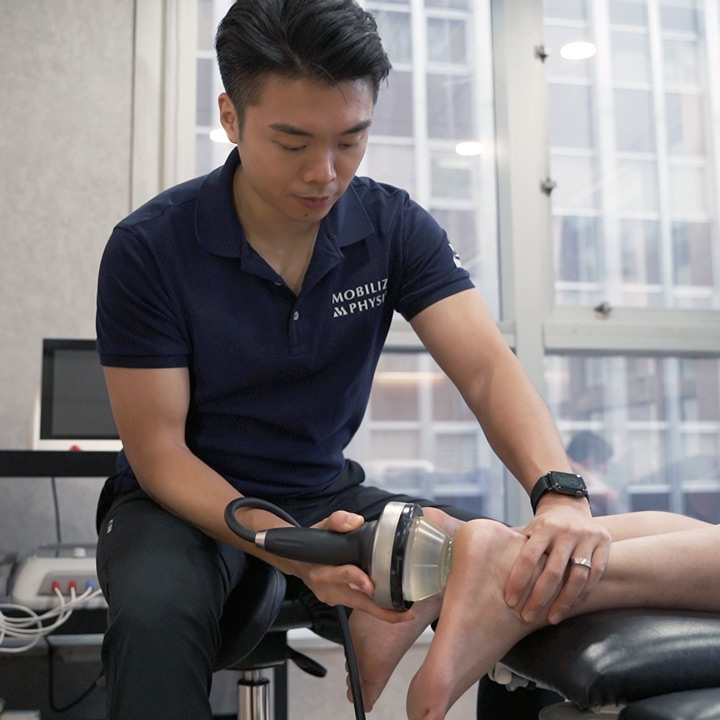

Physiotherapy Service
Mobilize Physio is a physiotherapy center located in Hong Kong. Our team of professional physiotherapists provides high-quality, evidence-based pain treatment. Our services include sports injury treatment, pain management, post-surgery rehabilitation, and posture and body alignment correction.
Every patient is unique, and we believe that every treatment plan should be customized accordingly. Therefore, we focus on one-on-one service to ensure that each patient receives personalized attention and specialized care. Contact us today to learn more about our physiotherapy services.
Latest Blog Posts
Standing All Day at Work? 7 Tips to Reduce Your Risk of Varicose Veins

Mobility Enhancement for Older Adults: The Key to Healthy Aging
Traditional Acupuncture vs. Dry Needling: What’s the Difference?

Are You a Runner Experiencing Knee Pain? Here’s Why and What You Can Do

A Must-Read for Beginner Skiers! 6 Common Skiing Injuries and How to Prevent Them

Sinuses and Neck Pain: Is There a Connection?