Understanding shoulder pain is crucial for effectively managing and preventing it. The shoulder is a complex and highly mobile joint, making it susceptible to various injuries and conditions. Addressing shoulder pain promptly is essential for maintaining mobility and overall quality of life. This comprehensive guide will delve into the causes of shoulder pain, symptoms, diagnostic methods, quick fixes, long-term treatments, and preventive measures to help you navigate and alleviate this common issue.
Anatomy of the Shoulder
The shoulder is a ball-and-socket joint comprising three bones: the humerus (upper arm bone), scapula (shoulder blade), and clavicle (collarbone). This joint’s intricate structure includes muscles, tendons, and ligaments that provide stability and a wide range of motion. Understanding the basic anatomy of the shoulder helps in identifying the common points of injury, which often involve the rotator cuff, the group of muscles and tendons that stabilize the shoulder.
Common Causes of Shoulder Pain
Causes of shoulder pain can be varied and complex. Some of the most frequent include:
Injuries and Trauma
- Dislocation: This occurs when the upper arm bone pops out of the shoulder socket, causing intense pain and stiffness.
- Rotator Cuff Tears: Tears in the rotator cuff can be partial or complete and often result from overuse or acute injury, leading to significant pain and weakness.
Overuse and Repetitive Motion
- Tendonitis/tendinopathy: Inflammation and degeneration of the tendons, often due to repetitive motion, causing pain and tenderness around the joint.
- Bursitis: Inflammation of the bursa, a fluid-filled sac that reduces friction, leading to pain and swelling.
Degenerative Conditions
- Arthritis: This can affect the shoulder joint, leading to pain, stiffness, and reduced range of motion over time.
Referred Pain
- Heart Issues: Sometimes shoulder pain can be a symptom of heart problems, such as a heart attack.
- Gallbladder Problems: Conditions like gallstones can cause referred pain in the shoulder.
- Cervicogenic referred pain: the cervical spine (neck) can also refer pain to the shoulder region.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Recognizing the symptoms and diagnosis of shoulder pain is vital for effective treatment. Common symptoms include:
Typical Symptoms
- Pain Types and Locations: Pain can be sharp, dull, or burning and may be located in the front, back, or side of the shoulder.
- Stiffness and Weakness: Difficulty moving the shoulder and weakness in the arm are common.
Diagnostic Methods
- Physical Examination: A healthcare provider will assess range of motion, strength, and areas of tenderness.
- Imaging Tests: X-rays, MRI, and ultrasound can provide detailed images to identify injuries like rotator cuff tears or dislocation.
Quick Fixes and Immediate Relief
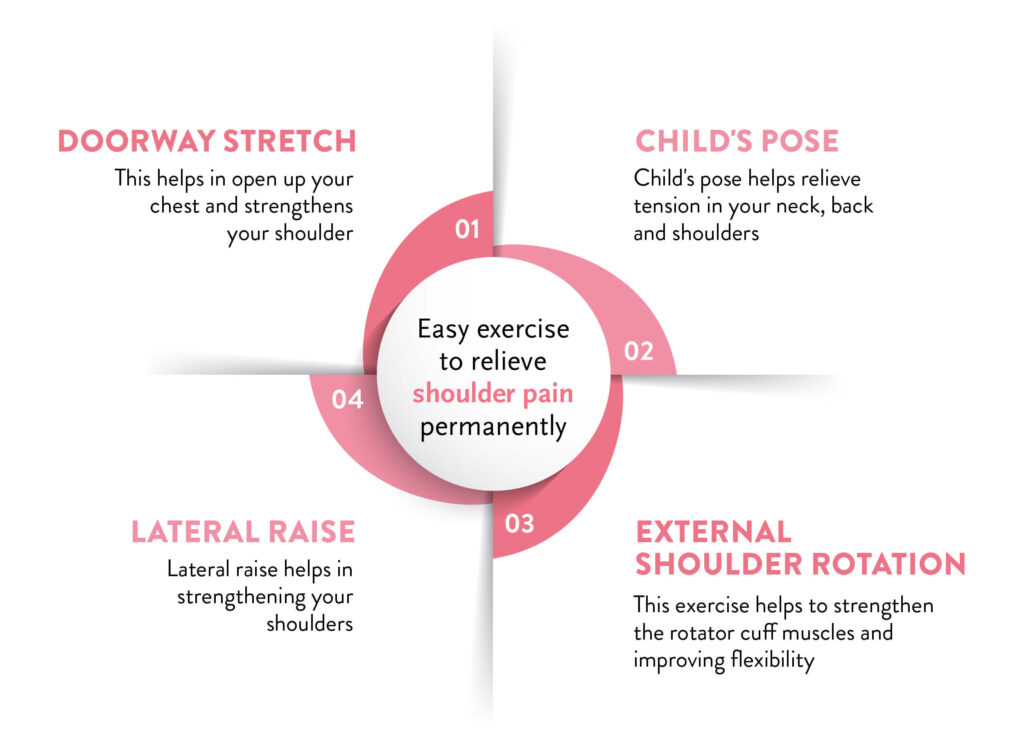
When dealing with shoulder pain, immediate relief can often be achieved through several methods:
Rest and Activity Modification
- Limiting activities that exacerbate pain can prevent further injury and promote healing.
Ice and Heat Application
- Ice can reduce swelling and numb sharp pain, while heat can relax muscles and improve blood flow to the area.
Over-the-Counter Pain Relief
- Medications such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen can help reduce pain and inflammation.
Physical Therapy Exercises
- Gentle exercises and stretches can maintain mobility and strengthen the shoulder, aiding in recovery.
Long-Term Management and Treatment
For persistent shoulder pain, long-term management and treatment options include:
Medications
- Prescription anti-inflammatory drugs or pain relievers can help manage chronic pain.
Injections
- Corticosteroid injections can reduce inflammation and provide significant pain relief for conditions like bursitis or tendonitis.
Surgery Options
- In severe cases, surgical interventions such as arthroscopy or rotator cuff repair may be necessary.
Lifestyle Adjustments and Ergonomics
- Making ergonomic adjustments at work and in daily activities can help prevent further strain on the shoulder.
Preventive Measures
Preventing shoulder pain involves proactive measures:
Proper Exercise Techniques
- Using correct form and avoiding overexertion during exercise can prevent injuries.
Workplace Ergonomics
- Adjusting the setup of workstations to reduce strain on the shoulders is crucial.
Regular Stretching and Strengthening
- Incorporating stretching and strengthening exercises into your routine can maintain shoulder health and prevent pain.
When to Seek Professional Help
Knowing when to seek professional help for shoulder pain is important:
Signs of Serious Conditions
- Severe pain, sudden swelling, or an inability to move the shoulder warrants immediate medical attention.
When to Visit a Healthcare Provider
- Persistent pain lasting for more than a few weeks, especially if it interferes with daily activities, should be evaluated by a healthcare provider.
Conclusion
Understanding shoulder pain, its causes, symptoms, and treatment options is essential for effective management and prevention. By recognizing the signs and implementing both immediate and long-term strategies, you can alleviate pain and maintain shoulder health. If you’re struggling with shoulder pain, consider seeking the expertise of healthcare professionals like Mobilize Physio, who can provide personalized care and guidance to help you regain function and improve your quality of life.