Common Conditions
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
Types, Symptoms and Treatments
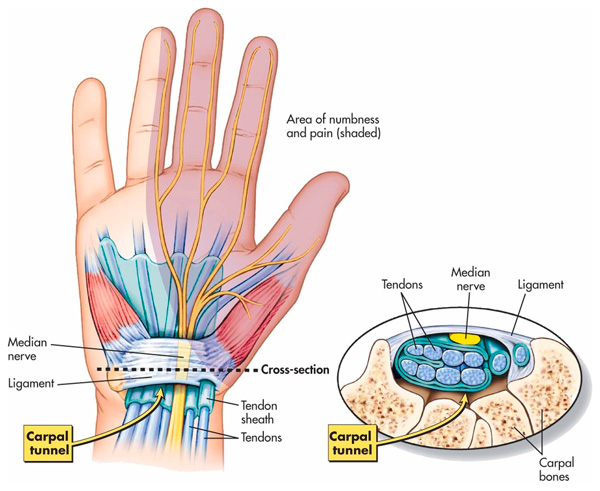
Understanding Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS), is a condition caused by compression of the median nerve as it passes through the carpal tunnel in the wrist. Patients may experience pain, numbness, and tingling in the hand or fingers, and in severe cases, it can even affect daily activities. This condition is common in professions that require prolonged repetitive use of the hands and wrists, such as office workers (especially those who type for long periods), carpenters, hairdressers, cleaners, and restaurant or kitchen workers.
Repeated strain on the tendons of the wrist and hand can lead to inflammation, reducing the available space within the carpal tunnel, which results in compression of the tendons and nerves, leading to irritation of the median nerve. Since the median nerve is essential for providing sensation and strength to the hand, its compression can cause discomfort and affect normal hand function.
Symptoms of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
Carpal tunnel syndrome symptoms typically develop gradually and may worsen over time:
- Numbness or tingling in the fingers (thumb, index, middle, and ring fingers) and palm
- Hand weakness, difficulty gripping objects
- Pain or discomfort that worsens at night or with repetitive use
- A “shock-like” sensation radiating from the wrist to the fingers
- Clumsiness or difficulty performing fine motor tasks
Causes and Risk Factors
Several factors can contribute to carpal tunnel syndrome, including:
- Repetitive Hand Movements: Typing, prolonged mouse use, playing musical instruments, or manual labour
- Wrist Positioning: Prolonged wrist flexion or poor ergonomics
- Medical Conditions: Diabetes, hypothyroidism, rheumatoid arthritis, and pregnancy-related fluid retention
- Genetics: Some individuals naturally have a smaller carpal tunnel, increasing the risk of nerve compression

